Live carbon insight - turn mandatory LCA's into your competitive edge in Archicad
Built for architects, Anavitor LCA’s two-way integration makes it easy to keep life-cycle impact up to date with every change, feeding high-precision LCA data straight back into your BIM model.
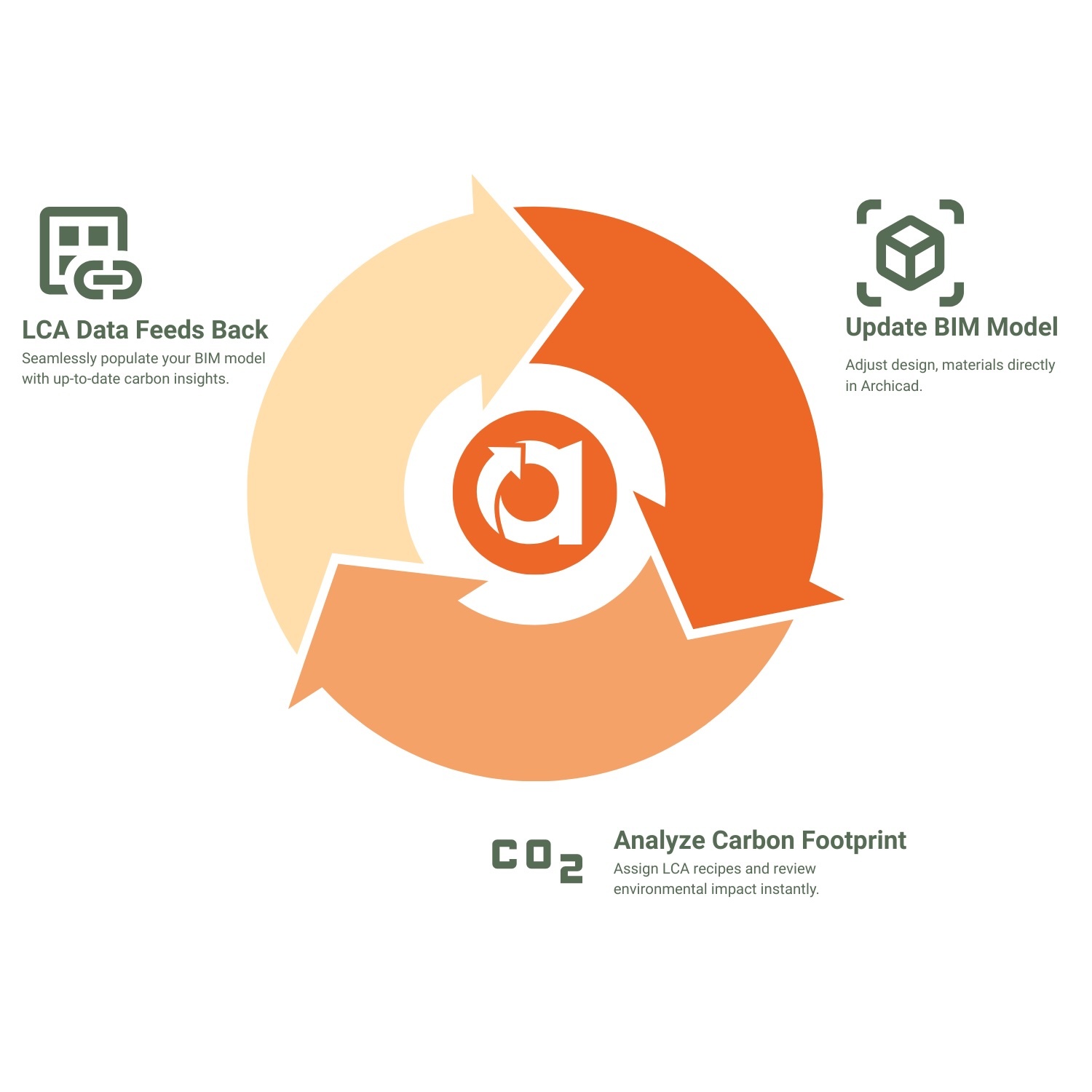
Make LCA part of the design – not an afterthought
LCA is often applied too late—when design decisions are already locked in and changes become expensive or limited in impact. This delay reduces your ability to improve a project’s climate performance when it matters most.
Anavitor LCA puts LCA where it belongs—early in the design process.
Fully integrated with Archicad, Anavitor lets you run high-precision carbon footprint calculations as you design. Your model stays updated as results flow seamlessly back into your BIM environment.
No exporting. No waiting. No disruption.
Smarter, climate-conscious decisions—built into your everyday workflow.
Turn compliance into a strategic advantage
Anavitor transforms mandatory LCA reporting into a competitive tool. By embedding precise life-cycle data directly in your BIM model, you gain full control and visibility—helping you meet regulations, win clients, and lead with sustainability.
CLIENT SUCCESS
"At Skanska, we use Anavitor, which seamlessly integrates economic calculations with climate calculations. This tool allows estimators and project managers to evaluate both costs and climate impacts of different measures, enabling us to make informed decisions that balance financial and environmental considerations."


"As the requirements for our carbon emissions become stricter, our responsibility also becomes clearer."
![]()

"We aim to be industry leaders in the green shift. Being able to offer climate calculations is a way for us to strengthen our environmental offerings to our customers."
.jpg?width=100&height=100&name=Veidekke-logo_(JPG).jpg)


STAY UPDATED - SIGN UP FOR OUR NEWSLETTER
Keep ahead in LCA: Building industry news straight to you inbox.
See how high-precision LCA transforms your workflow
Experience firsthand how Anavitor's exclusive two-way integration simplifies sustainability analysis while enhancing your BIM deliverables. Our 30-minute personalized demo shows exactly how your projects benefit from embedded carbon intelligence.
Select a convenient time below to see the only architect-driven LCA solution for Archicad in action.
What we have to say
Frequently asked questions about LCA
The key components and stages of a typical Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) process involve a comprehensive approach to evaluating the environmental impacts of a product or system throughout its life cycle. These stages include:
Goal and Scope Definition: Establishing the LCA's purpose, the system to be assessed, and the boundaries of the study.
Inventory Analysis (Life Cycle Inventory, LCI): Compiling data on the inputs and outputs associated with the product's life cycle, including raw material extraction, energy use, water use, emissions, and waste.
Impact Assessment (Life Cycle Impact Assessment, LCIA): Evaluating the environmental impacts of the inputs and outputs identified in the LCI, often focusing on categories like global warming potential, resource depletion, and ecological toxicity.
Interpretation: Analyzing the results to make informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, and communicate findings.
Each stage is crucial in understanding and minimizing the environmental impacts associated with the entire life cycle of the product or system.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) can profoundly influence decision-making in construction and architectural design by providing a detailed analysis of the environmental impacts associated with different materials, methods, and design choices. Architects and builders use LCA data to:
- Select Materials: Choose building materials with lower environmental footprints, such as those requiring less energy to produce or those made from recycled content.
- Design Efficiently: Opt for architectural designs that reduce energy consumption, improve water efficiency, and minimize waste during construction and throughout the building's lifecycle.
- Assess Overall Impact: Evaluate the total environmental impact of a project, including greenhouse gas emissions, pollution, and resource depletion, guiding more sustainable design decisions.
- Meet Certification Standards: Align projects with sustainability standards required for certifications like LEED or BREEAM, enhancing the building's marketability and compliance with regulations.
- Inform Stakeholders: Provide transparent information to stakeholders, clients, and the public about the environmental considerations and sustainability efforts incorporated into the project.
By integrating LCA in the early stages of design and construction, professionals can make more informed, responsible choices that lead to sustainable, eco-friendly, and cost-effective buildings.
Yes, there are several industry standards and certifications related to Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) in building projects, which help ensure sustainability and environmental responsibility in construction and design. Key among them are:
-
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design): A widely recognized green building certification program that considers LCA in its criteria, particularly in materials selection and resource efficiency.
-
BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method): Another prominent certification that evaluates the sustainability of buildings, incorporating LCA to assess the environmental impact of building materials and processes.
-
ISO 14040 and ISO 14044: International standards providing guidelines and principles for conducting LCAs, including framework, methodology, and reporting.
-
Green Star: A certification program used primarily in Australia and New Zealand, which includes LCA as part of its criteria for assessing the sustainability of building projects.
-
DGNB (German Sustainable Building Council): A certification system that uses LCA to evaluate the environmental, economic, and social sustainability aspects of buildings.
These certifications and standards not only guide the construction industry towards more sustainable practices but also provide benchmarks for assessing the environmental performance of building projects.
Industry standards and certifications play a crucial role in integrating Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) into sustainable building practices by establishing clear guidelines and benchmarks for environmental performance. These certifications, such as LEED, BREEAM, and DGNB, require or highly encourage the use of LCA in the assessment of a building's overall environmental impact. By adhering to these standards, architects and builders are motivated to adopt LCA as a key tool in their design and construction processes. This not only helps in quantifying and reducing the ecological footprint of buildings but also in achieving recognized sustainability credentials, thereby elevating the building's market value and reputation. These standards effectively bridge the gap between theoretical environmental conservation principles and practical implementation in the building industry.